What
Is BPH?
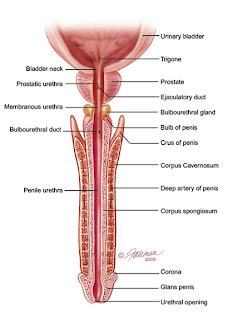 Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH),
additionally called Benign growth of the prostate (Bep), adenofibromyomatous
hyperplasia and considerate pro-static hypertrophy (in fact wrong utilization),
is an expansion in size of the prostate.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH),
additionally called Benign growth of the prostate (Bep), adenofibromyomatous
hyperplasia and considerate pro-static hypertrophy (in fact wrong utilization),
is an expansion in size of the prostate.
BPH includes hyperplasia
of prostatic stromal and epithelial cells, bringing about the creation of
expansive, decently discrete knobs in the periurethral locale of the prostate.
The point when sufficiently great, the knobs pack the urethral waterway to
reason fractional, or at times practically finish, deterrent of the urethra,
which meddles with the standard stream of pee. It expedites side effects of
urinary reluctance, continuous pee, dysuria (tormenting pee), expanded danger
of urinary tract contaminations, and urinary maintenance. In spite of the fact
that prostate particular antigen levels may be raised in the aforementioned
patients on account of expanded organ volume and aggravation because of urinary
tract contaminations, Bph does not accelerate disease or increment the danger
of cancer.[citation needed]
BPH includes hyperplasia
(an expansion in the amount of cells) as opposed to hypertrophy (a development
in the span of unique units), yet the two terms are regularly utilized
conversely, even around urologists.
Adenomatous prostatic
development is accepted to start at pretty nearly age 30 years. An expected 50%
of men have histologic proof of BPH by age 50 years and 75% by age 80 years; in
40–50% of the aforementioned men, BPH comes to be clinically significant.
What Are The Factors Leads to BPH?
Hazard calculates for
advancing BPH incorporate:
- Obesity
- Lack of physical movement
- Erectile brokenness
- Increasing age
- Prior Family history of BPH
BPH: Signs and Symptoms
Benign
prostatic hyperplasia indications are ordered as space or voiding.
Space manifestations
incorporate urinary recurrence, direness (forcing need to void that can't be
conceded), earnestness incontinence, and voiding around evening time
(nocturia).
Voiding manifestations
incorporate urinary stream reluctance (expecting to hold up for the stream to
start), discontinuity (when the stream begins and stops irregularly), straining
to void, and spilling. Torment and dysuria are normally not show. The
aforementioned space and voiding side effects are assessed utilizing the
International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) poll, outlined to evaluate the
intensity of BPH.
BPH could be a dynamic
infection, particularly if left untreated. Deficient voiding brings about
stasis of microscopic organisms in the bladder deposit and an expanded danger
of urinary tract tainting. Urinary bladder stones are framed from the
crystallization of salts in the lingering pee. Urinary maintenance termed
intense or perpetual, is an additional type of movement. Intense urinary
maintenance is the powerlessness to void, while in ceaseless urinary
maintenance the leftover urinary volume bit by bit builds, and the bladder
extends. This can bring about bladder hypotonia. A few patients who experience
constant urinary maintenance might in the end advancement to renal washout, a
condition termed obstructive uropathy.
BPH: What Causes BPH
Most masters acknowledge
androgens (testosterone and identified hormones) to assume a lenient part. This
implies that androgens must be available for BPH to happen, however don't
fundamentally straight make the condition. This is underpinned by the way that
emasculated young men don't improve BPH when they age. Furthermore, managing
exogenous testosterone is not connected with a noteworthy build in the danger
of BPH symptoms. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a metabolite of testosterone, is a
basic middle person of prostatic development. DHT is integrated in the prostate
from coursing testosterone by the movement of the compound reeducates, type 2.
This compound is restricted primarily in the stromal units; subsequently, those
units are the essential site for the blend of DHT
Testosterone advertises
prostate unit proliferation, yet moderately level levels of serum testosterone
are discovered in patients with BPH. One minor study has indicated that
restorative emasculation brings down the serum and prostate hormone levels
unevenly, having less impact on testosterone and di-hydro-testosterone levels
in the prostate.
BPH : Some of The Medical Science Treatments Avail for BPH
Watchful Waiting/Active
Surveillance
This medication choice is
handy for patients who have mellow manifestations of BPH or have direct to
extreme side effects yet are not disturbed by their indications. Patients
experiencing kidney issues as a consequence of BPH, urinary maintenance
(without warning being unable to urinate), or incessant pee contaminations, and
urinary incontinence are bad contestants for this medicine choice.
Throughout watchful
holding up, a patient is nearly followed by his doctor yet he doesn't
appropriate any dynamic medicine. Numerous patients' side effects might be
regulated or maintained by adapting their present prescriptions and diet.
Patients will be examined yearly, and discoveries from the tests will be
utilized to verify if extra medicine is required to control a patient's BPH.
Alternative Treatment Available for BPH
Therapeutic Therapies
- Alpha blockers
- 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors
- Transurethral needle Ablation (Tuna) of the prostate
- Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT)
Surgical Techniques
There are numerous surgical
strategies to treat BPH. Surgery is the most obtrusive methodology and is
normally held for patients experiencing direct to extreme BPH identified LUTS
or intricacies which go out from BPH (e.g. urinary maintenance, orderly LUTS,
repetitive pee tainting). It is usually held for patients who have not had the
ability to truly treat the condition with other medication choices or for those
who give direct to intense BPH. The accompanying are the ordinarily
acknowledged surgical medication choices:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
- Open prostatectomy


No comments:
Post a Comment